Definition
Odontogenic cyst associated with unerupted tooth in young adults.
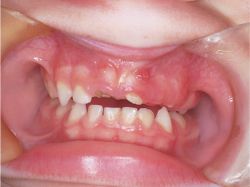
Clinical Features
Usually young adult
Symptoms:
swelling
rarely, pain
occur late or with infection and inflammation
PathogenesisOdontogenic:
arises from alterations of reduced enamel epithelium after development of enamel
Gross Pathology
Surround or associated with unerupted teeth
Associated with the tooth crown, at least initially
Present in almost 1% of individuals having complete dental radiographs1–3
Histopathology
Thin fibrous wall lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium1
Secondary changes common in form of:
chronic inflammation
ulceration
reactive hyperplasia
metaplasia
calcification
clusters of histiocytes containing hemosiderin and lipofuscin2,4
Dysplasia and carcinoma can develop5–7
Differential Diagnosis
Select up to 2 differential diagnoses to compare with Dentigerous Cyst
Odontogenic Keratocyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Eruption Cyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Radicular Cyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Other epithelium-lined cysts of maxilla or mandible8–12
Management
Treatment: Surgical enucleation. All dentigerous cysts should be submitted for histopathologic examination.
Prognosis: Good
Differential diagnosis: Cystic ameloblastoma, odontogenic keratocyst, odontogenic adenomatoid tumor and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
Odontogenic cyst associated with unerupted tooth in young adults.
Clinical Features
Usually young adult
Symptoms:
swelling
rarely, pain
occur late or with infection and inflammation
PathogenesisOdontogenic:
arises from alterations of reduced enamel epithelium after development of enamel
Gross Pathology
Surround or associated with unerupted teeth
Associated with the tooth crown, at least initially
Present in almost 1% of individuals having complete dental radiographs1–3
Histopathology
Thin fibrous wall lined by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium1
Secondary changes common in form of:
chronic inflammation
ulceration
reactive hyperplasia
metaplasia
calcification
clusters of histiocytes containing hemosiderin and lipofuscin2,4
Dysplasia and carcinoma can develop5–7
Differential Diagnosis
Select up to 2 differential diagnoses to compare with Dentigerous Cyst
Odontogenic Keratocyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Eruption Cyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Radicular Cyst [Mandible and Maxilla] (View full diagnosis)
Other epithelium-lined cysts of maxilla or mandible8–12
Management
Treatment: Surgical enucleation. All dentigerous cysts should be submitted for histopathologic examination.
Prognosis: Good
Differential diagnosis: Cystic ameloblastoma, odontogenic keratocyst, odontogenic adenomatoid tumor and calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor













0 comments:
Post a Comment